20 Things Every Business Owner Should Know About CyberSecurity
Cybersecurity is a critical concern for businesses of all sizes in today’s digital age. Here are ten crucial things every business owner should know about cybersecurity:
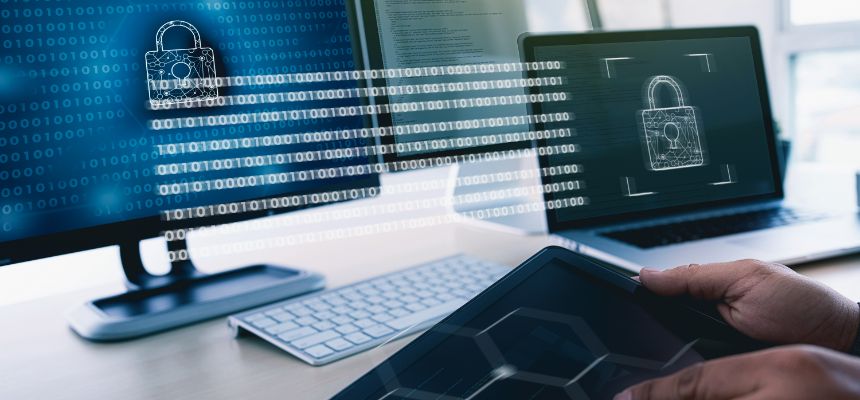

Cybersecurity is a critical concern for businesses of all sizes in today’s digital age. Here are ten crucial things every business owner should know about cybersecurity:

Understand that cyber threats can have severe consequences for your business. Threats include data breaches, ransomware attacks, phishing, and more. It's not a matter of "if" but "when" your business may face a cyber incident.
Allocate budget and resources for cybersecurity measures. This includes investing in robust antivirus software, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security assessments.
Employees are often the weakest link in cybersecurity. Provide comprehensive training to your staff on recognizing and responding to cyber threats, including phishing attempts.
Protect sensitive customer and company data. Implement data encryption, access controls, and regular data backups to prevent data loss in case of an incident.
Encourage strong, unique passphrases for all accounts and implement password policies that require regular updates. Also, always use multi-factor authentication (MFA) for added security.
Keep all software and hardware up-to-date with security patches. Cybercriminals often exploit known vulnerabilities in outdated systems.
Develop and maintain an incident response plan that outlines how your business will react to a cybersecurity breach. Ensure employees know their roles in case of an incident.
Be aware of the cybersecurity practices of third-party vendors and partners. A breach in their system can affect your business. Consider including cybersecurity clauses in contracts.
Stay informed about cybersecurity regulations that apply to your industry, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA. Ensure your business complies with the relevant laws and regulations.
Cybersecurity is not a one-time effort; it requires constant monitoring and adaptation. Regularly assess your security posture and make necessary improvements as threats evolve.
Consider purchasing cyber insurance. This can help cover the financial costs associated with a cyber incident, including legal fees, notification costs, and data recovery.
With the increase in remote work, ensure remote employees have secure access to your network and follow best practices for securing their home offices.
Establish a patch management process to ensure timely updates and security patches for all software and systems. This can help prevent known vulnerabilities from being exploited.
Evaluate the cybersecurity practices of your suppliers and vendors, as their weaknesses can impact your business. Ensure they have security measures in place.
Encrypt sensitive data, both in transit and at rest. Encryption can protect your data even if it falls into the wrong hands.
Regularly back up your data and test the restoration process. A reliable backup can be crucial in recovering from a ransomware attack or data loss.
Educate your employees about social engineering attacks, like phishing and pretexting. These attacks often rely on manipulating people rather than technology.
Foster a culture of cybersecurity awareness within your organization. Make sure employees at all levels understand the importance of security.
Implement a multi-layered security approach, including firewalls, antivirus, intrusion detection, and security policies, to provide comprehensive protection.
Your cybersecurity needs may change as your business grows. Be prepared to scale your cybersecurity measures to accommodate expansion. By taking these steps and staying proactive in your approach to cybersecurity, you can significantly reduce the risk of cyber threats and protect your business, customers, and reputation. Remember that cybersecurity is ongoing, and staying informed about emerging threats and best practices is essential.
Small businesses often have limited resources and expertise when it comes to cybersecurity. However, they must protect their sensitive data and maintain the trust of their customers. Here are some valuable cybersecurity resources tailored to the needs of small businesses:
CISA, a federal agency under the U.S. Department of Homeland Security, provides resources, guides, and tools to help small businesses improve their cybersecurity posture. Visit their Small Business page for valuable information.
The FTC offers resources on protecting your business and customers from cyber threats, including articles, guides, and videos. Their "Small Business Computer Security Basics" is a good starting point.
NIST's Cybersecurity Framework provides a comprehensive guide for improving cybersecurity, including guidelines for identifying, protecting, detecting, responding to, and recovering from cybersecurity incidents. You can adapt the NIST policies to the specific needs of small businesses.
Many SBDCs across the United States offer free or low-cost cybersecurity training, workshops, and one-on-one counseling to help small businesses strengthen their security measures.
StaySafeOnline, powered by the National Cyber Security Alliance, offers a range of cybersecurity resources and tools specifically designed for small businesses. Their "CyberSecure My Business" program is a valuable resource.
The SBA provides information and resources for small businesses, including cybersecurity advice and tips. You can find articles and guidance on their website.
The BBB offers information on cybersecurity best practices and how to safeguard your business from online threats. They also have scam alerts to keep businesses informed about the latest scams.
If you have cyber insurance, your provider may offer resources and tools to help you mitigate and respond to cyber threats. Contact your insurer to see what resources they can provide.
Some local governments and municipalities offer resources and support to help small businesses improve their cybersecurity. Check with your local government or chamber of commerce for information.
Consider working with an MSP specializing in small business cybersecurity. They can offer expertise and managed security services tailored to your budget and needs.
Some universities and colleges offer free or low-cost cybersecurity training and workshops for small businesses. Check with local educational institutions for opportunities.
Depending on your industry, specific associations or organizations may provide cybersecurity resources and guidelines for small businesses within that sector.
Online platforms like Coursera, edX, and LinkedIn Learning offer cybersecurity courses to help small business owners and employees gain essential knowledge and skills.
Remember that cybersecurity is ongoing, and staying informed about emerging threats and best practices is essential. Small businesses should prioritize cybersecurity and use these resources to enhance their defenses against cyber threats.