What is biometric authentication?
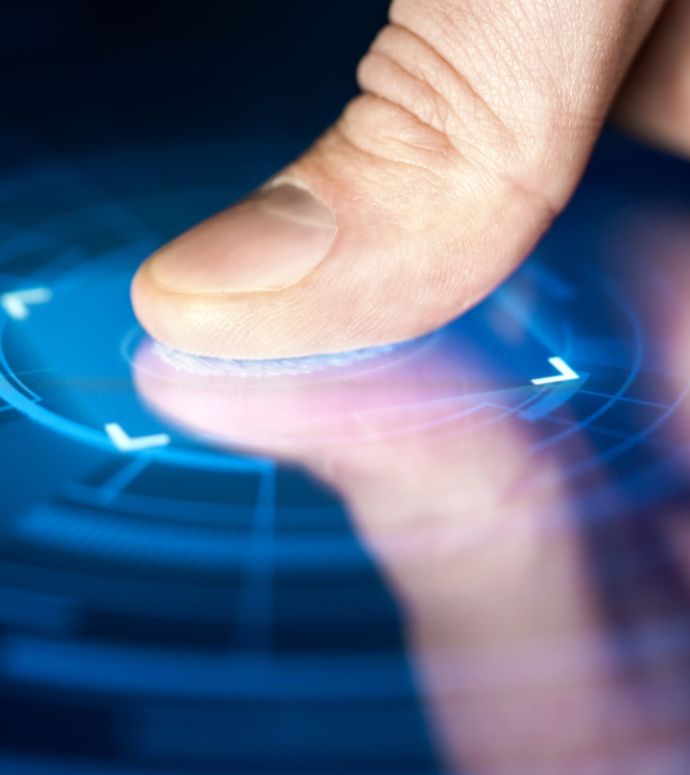
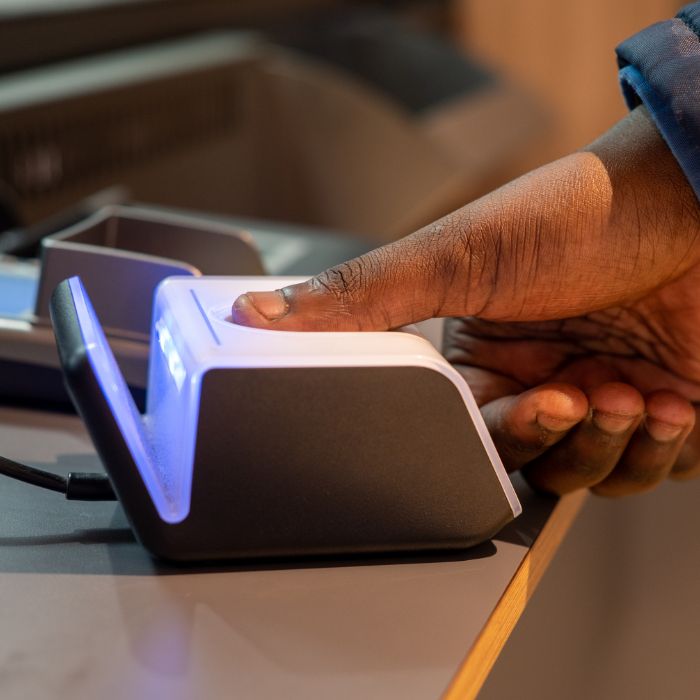
Biometric authentication refers to verifying an individual’s identity by using their unique physical or behavioral characteristics. It relies on the notion that each person possesses distinct and difficult-to-replicate biometric traits. These traits include fingerprints, iris patterns, facial features, voice patterns, hand geometry, and behavioral characteristics such as typing, rhythm, or gait.
The authentication process typically involves capturing an individual’s biometric data using a specialized device, such as a fingerprint scanner, iris scanner, or facial recognition camera. This data is compared against previously recorded biometric information stored in a database or device. If the captured biometric data matches the stored data within an acceptable threshold, the individual’s identity is verified, and access is granted.
Biometric authentication offers several advantages over traditional authentication methods such as passwords or PINs. Biometric traits are unique to individuals and difficult to forge, making it harder for unauthorized individuals to gain access. They also eliminate the need for individuals to remember and manage complex passwords, which can improve convenience and security.
However, it’s important to note that biometric authentication systems are not foolproof. Biometric data can be compromised if it is not adequately protected, and there have been cases where certain biometric traits have been successfully spoofed or replicated. As with any security measure, it is essential to implement appropriate safeguards and combine biometric authentication with other security measures for robust protection.